On April 20, Huawei announced that it was replacing its "legacy ERP system" with its own MetaERP system, which is "in full control." The outdated system was supplied by the American software company Oracle.
Oracle defines ERP as "a type of software that organizations use to manage day-to-day business operations such as accounting, procurement, project management, risk and compliance management, and supply chain operations."
It says: "Enterprise Performance Management in a complete ERP suite, software that helps plan, budget, forecast and report on an organization's financial performance."
Huawei calls ERP "the most important IT management system in an enterprise." This was significant when Oracle was forced to stop providing software updates and technical services to Huawei in May 2019 after the US Commerce Department's Bureau of Industry and Security added Huawei to its list of entities.
Tao Jingwen, Huawei's President of Quality, Business Process and IT Management, said: “More than three years ago, we separated from our legacy ERP system and other core operational and management systems. Since then, we have not only been able to build our own MetaERP, but also manage the transition and prove its capabilities. Today we are proud to announce that we have broken the blockade. We survived.
Huawei's announcement included the following statement: “Huawei today held the MetaERP Awards to recognize individuals and teams who have made significant contributions to this project. The event titled "Heroes Struggle to Cross the Dadu River" was held at the campus of Shi Liu Bei Po Village in Dongguan City, China.

Huawei has a new in-house ERP system. Photo: Twitter
In addition to thousands of employees, Chinese partner companies including Qi An Jin Technology, Kingdi International Software and Kingsoft contributed to the project.
Qi An Jin is one of the largest cyber security companies in China. Kingdee is one of the largest ERP software providers in China. Kingsoft provides office, security and other software, as well as cloud computing services.
In 1935, the Chinese Communist Party's Red Army crossed the Dadu River in western Sichuan and defeated Nationalist forces at the Battle of Luding Bridge.
According to Tao Jingwen, "The lack of access to ERP has become the bane of Huawei, hindering our progress and threatening our existence."
According to Huawei, “The old ERP system was the core system based on Huawei's corporate activities and rapid development for more than 20 years. It supports Huawei's efficient business operations in more than 170 countries and regions around the world, which generate tens of billions of dollars in revenue every year."
In 2016, Huawei and Oracle agreed to deepen cooperation using the Huawei KunLun Mission Critical server and Oracle database platform technology.
In 2017, they announced the Power IoT Ecosystem Partnership for advanced metering infrastructure and smart grid software. But after that, relations deteriorated.
In 2019, Oracle laid off about 900 of its roughly 1,600 employees, mostly researchers, at its research center in China, shortly after Huawei announced it was building its own database management software called GaussDB.
Then, when the US government ban kicked in, Huawei "decided to build a fully self-managed MetaERP system to replace the old ERP system."
According to Huawei, MetaERP currently handles 100% of business scenarios and 80% of Huawei's business volume. MetaERP has already passed monthly, quarterly and annual billing tests, making sure there are no errors, delays or accounting adjustments.”
China ERP
According to Chinese research and consulting firm Tenba Group, China's commercial ERP market will grow nearly 15% this year to $2.2 billion.
According to Tenba Group, the global ERP market will grow 11% to reach $55 billion, while China will account for only 4%. Given the size and complexity of the Chinese economy, China has been ahead of global markets for years.
According to Tenba, the two companies that own more than half of the ERP business are SAP and Oracle, the big Chinese companies, and the top seven vendors have about 90%. These companies.
SAP (33%) - Germany Oracle (20%) - USA Yongyo (14%) - China IBM (8%) - USA Kingdom (6%) - China Talosoft (5%) - China Information (3%) - USA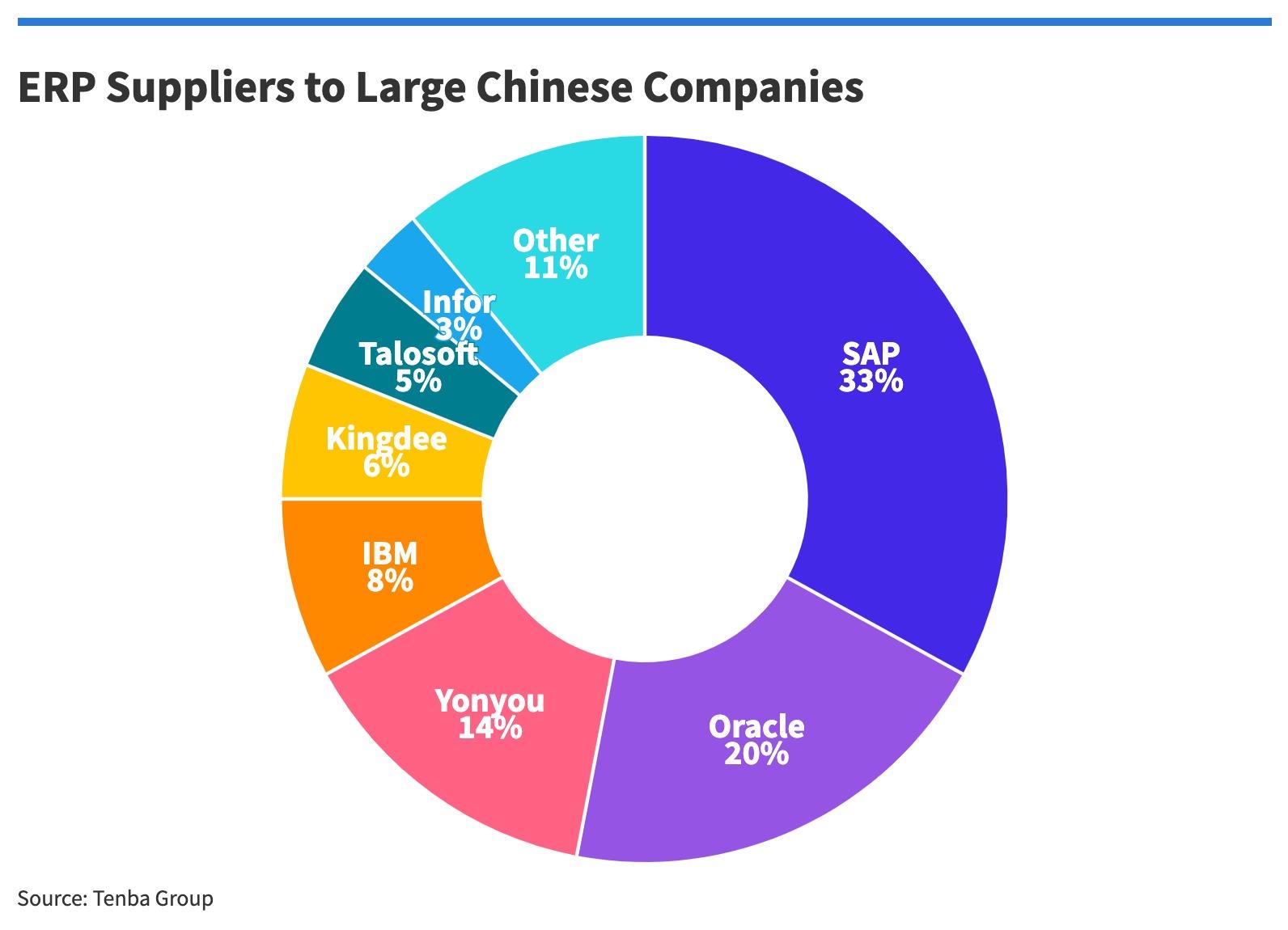
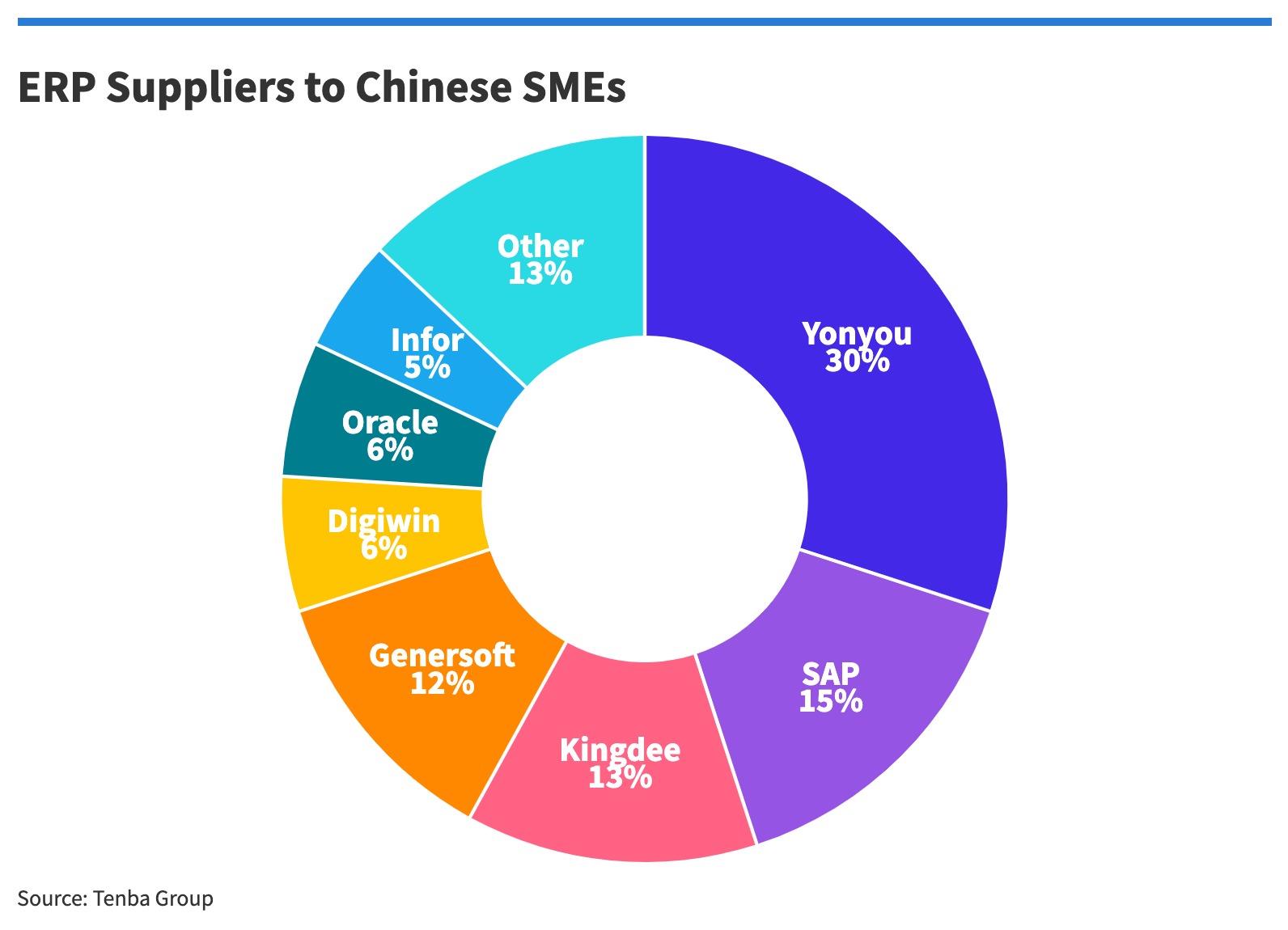
Most Chinese small and medium enterprises (SMEs) use in-house ERP providers, but SAP has about 15% of the market and Oracle has 6%.
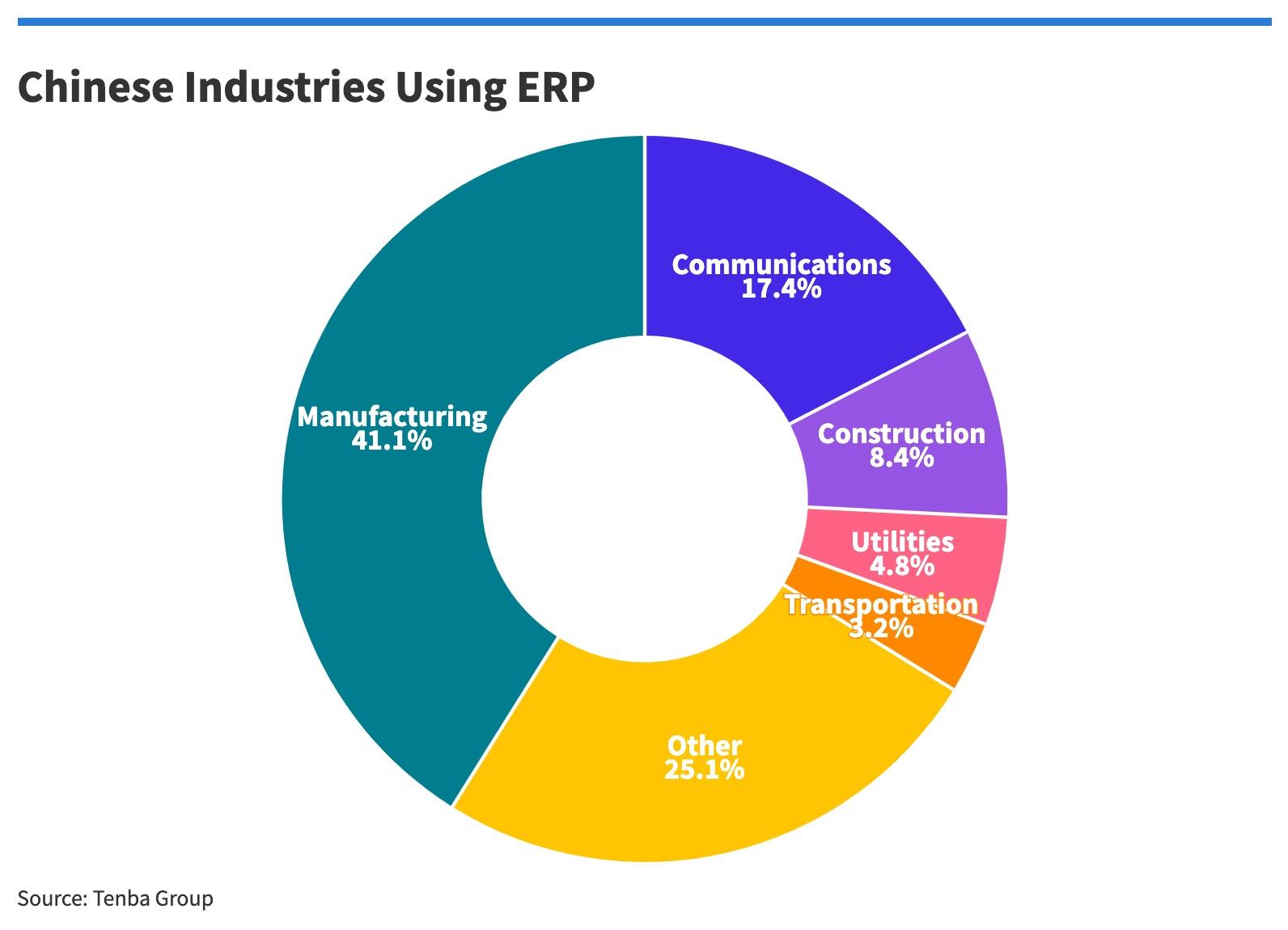
The most users of ERP in China are industry and communications, followed by construction, utilities and transportation.
SAP has been operating in China for 30 years. Now there are more than 6,500 employees, 100 official partners, 20,000 certified consultants and about 16,000 customers in the country.
In March, the president of SAP Greater China told China's state news agency Xinhua that "Chinese companies are becoming fully digital, connected and green, opening a window of opportunity for SAP in China."
"As a multinational company founded in Germany, SAP has developed its business in China thanks to China's deepening reforms, openness and rapid economic development. In fact, the market share numbers back it up.
Currently, Huawei has its own ERP software, while SAP is the largest ERP software provider in China, with Oracle in second place. This creates a unique dual objective for the US government, which is the expected outcome when the government's trade strategy favors sensitive behavior over the profit motive.
Subscribe to this author
Twitter: @ScottFo83517667


Post a Comment